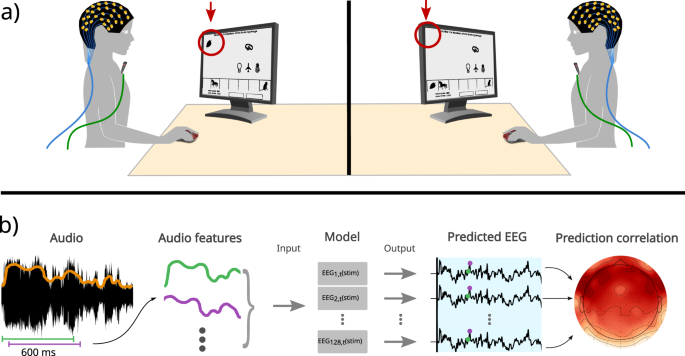
Speech-induced suppression during natural dialogues
Matin, E. Saccadic suppression: a review and an analysis. Psychol. Bull. 81, 899 (1974).
Blakemore, S.-J., Wolpert, D. M. & Frith, C. D. Central cancellation of self-produced tickle sensation. Nat. Neurosci. 1, 635–640 (1998).
Thiele, A., Henning, P., Kubischik, M. & Hoffmann, K.-P. Neural mechanisms of saccadic suppression. Science 295, 2460–2462 (2002).
Hughes, G., Desantis, A. & Waszak, F. Mechanisms of intentional binding and sensory attenuation: the role of temporal prediction, temporal control, identity prediction, and motor prediction. Psychol. Bull. 139, 133 (2013).
Curio, G., Neuloh, G., Numminen, J., Jousmäki, V. & Hari, R. Speaking modifies voice-evoked activity in the human auditory cortex. Hum. Brain Mapp. 9, 183–191 (2000).
Houde, J. F., Nagarajan, S. S., Sekihara, K. & Merzenich, M. M. Modulation of the auditory cortex during speech: an meg study. J. Cognit. Neurosci. 14, 1125–1138 (2002).
Scheerer, N. E., Behich, J., Liu, H. & Jones, J. A. Erp correlates of the magnitude of pitch errors detected in the human voice. Neuroscience 240, 176–185 (2013).
Wang, J. et al. Action planning and predictive coding when speaking. Neuroimage 91, 91–98 (2014).
Whitford, T. J. Speaking-induced suppression of the auditory cortex in humans and its relevance to schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry Cognit. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 4, 791–804 (2019).
Creutzfeldt, O., Ojemann, G. & Lettich, E. Neuronal activity in the human lateral temporal lobe. ii. responses to the subjects own voice. Exp. Brain Res. 77, 476–489 (1989).
Eliades, S. J. & Wang, X. Neural substrates of vocalization feedback monitoring in primate auditory cortex. Nature 453, 1102–1106 (2008).
Ford, J. M., Roach, B. J. & Mathalon, D. H. Assessing corollary discharge in humans using noninvasive neurophysiological methods. Nat. Protocols 5, 1160–1168 (2010).
Obleser, J. & Kayser, C. Neural entrainment and attentional selection in the listening brain. Trends Cognit. Sci. 23, 913–926 (2019).
Poeppel, D. & Assaneo, M. F. Speech rhythms and their neural foundations. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 21, 322–334 (2020).
Carey, J. Brain facts: A primer on the brain and nervous system (ERIC, 1990).
Hickok, G. & Poeppel, D. Towards a functional neuroanatomy of speech perception. Trends Cognit. Sci. 4, 131–138 (2000).
Giraud, A.-L. & Poeppel, D. Cortical oscillations and speech processing: emerging computational principles and operations. Nat. Neurosci. 15, 511–517 (2012).
Du, Y., Buchsbaum, B. R., Grady, C. L. & Alain, C. Noise differentially impacts phoneme representations in the auditory and speech motor systems. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 111, 7126–7131 (2014).
Caplan, D. Why is broca’s area involved in syntax? Cortex 42, 469–471 (2006).
Grewe, T. et al. The emergence of the unmarked: A new perspective on the language-specific function of broca’s area. Hum. Brain Map. 26, 178–190 (2005).
Di Liberto, G. M., O’Sullivan, J. A. & Lalor, E. C. Low-frequency cortical entrainment to speech reflects phoneme-level processing. Curr. Biol. 25, 2457–2465 (2015).
Etard, O. & Reichenbach, T. Neural speech tracking in the theta and in the delta frequency band differentially encode clarity and comprehension of speech in noise. J. Neurosci. 39, 5750–5759 (2019).
Desai, M. et al. Generalizable eeg encoding models with naturalistic audiovisual stimuli. J. Neurosci. 41, 8946–8962 (2021).
Hamilton, L. S. & Huth, A. G. The revolution will not be controlled: natural stimuli in speech neuroscience. Lang. Cognit. Neurosci. 35, 573–582 (2020).
Lalor, E. C., Power, A. J., Reilly, R. B. & Foxe, J. J. Resolving precise temporal processing properties of the auditory system using continuous stimuli. J. Neurophysiol. 102, 349–359 (2009).
Lalor, E. C. & Foxe, J. J. Neural responses to uninterrupted natural speech can be extracted with precise temporal resolution. Eur. J. Neurosci. 31, 189–193 (2010).
Holdgraf, C. R. et al. Encoding and decoding models in cognitive electrophysiology. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 11, 61 (2017).
Crosse, M. J., Di Liberto, G. M., Bednar, A. & Lalor, E. C. The multivariate temporal response function (mtrf) toolbox: a matlab toolbox for relating neural signals to continuous stimuli. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 10, 604 (2016).
Crosse, M. J. et al. Linear modeling of neurophysiological responses to speech and other continuous stimuli: methodological considerations for applied research. Front. Neurosci. 15, 705621 (2021).
Lalor, E. C., Pearlmutter, B. A., Reilly, R. B., McDarby, G. & Foxe, J. J. The vespa: a method for the rapid estimation of a visual evoked potential. Neuroimage 32, 1549–1561 (2006).
Ehinger, B. V. & Dimigen, O. Unfold: an integrated toolbox for overlap correction, non-linear modeling, and regression-based eeg analysis. PeerJ 7, e7838 (2019).
Gravano, A. & Hirschberg, J. Turn-yielding cues in task-oriented dialogue. In Proceedings of the SIGDIAL 2009 Conference, 253–261 (Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2009).
Gravano, A. & Hirschberg, J. Turn-taking cues in task-oriented dialogue. Comput. Speech Lang. 25, 601–634 (2011).
Brusco, P., Vidal, J., Beňuš, Š. & Gravano, A. A cross-linguistic analysis of the temporal dynamics of turn-taking cues using machine learning as a descriptive tool. Speech Commun. 125, 24–40 (2020).
Abrams, D. A., Nicol, T., Zecker, S. & Kraus, N. Right-hemisphere auditory cortex is dominant for coding syllable patterns in speech. J. Neurosci. 28, 3958–3965 (2008).
Hamilton, L. S., Edwards, E. & Chang, E. F. A spatial map of onset and sustained responses to speech in the human superior temporal gyrus. Curr. Biol. 28, 1860–1871 (2018).
Hamilton, L. S., Oganian, Y. & Chang, E. F. Topography of speech-related acoustic and phonological feature encoding throughout the human core and parabelt auditory cortex. BioRxiv https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.06.08.121624v1 (2020).
Oganian, Y. & Chang, E. F. A speech envelope landmark for syllable encoding in human superior temporal gyrus. Sci. Adv. 5, eaay6279 (2019).
Phillips, D. P. & Farmer, M. E. Acquired word deafness, and the temporal grain of sound representation in the primary auditory cortex. Behav. Brain Res. 40, 85–94 (1990).
Tallal, P., Miller, S. & Fitch, R. H. Neurobiological basis of speech: a case for the preeminence of temporal processing. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 682, 27–27 (1993).
Belin, P. et al. Lateralization of speech and auditory temporal processing. J. Cognit. Neurosci. 10, 536–540 (1998).
Liegeois-Chauvel, C., De Graaf, J. B., Laguitton, V. & Chauvel, P. Specialization of left auditory cortex for speech perception in man depends on temporal coding. Cereb. Cortex 9, 484–496 (1999).
Zatorre, R. J. & Belin, P. Spectral and temporal processing in human auditory cortex. Cereb. Cortex 11, 946–953 (2001).
Zaehle, T., Wüstenberg, T., Meyer, M. & Jäncke, L. Evidence for rapid auditory perception as the foundation of speech processing: a sparse temporal sampling fmri study. Eur. J. Neurosci. 20, 2447–2456 (2004).
Zatorre, R. J., Belin, P. & Penhune, V. B. Structure and function of auditory cortex: music and speech. Trends Cognit. Sci. 6, 37–46 (2002).
Scott, S. K., Blank, C. C., Rosen, S. & Wise, R. J. Identification of a pathway for intelligible speech in the left temporal lobe. Brain 123, 2400–2406 (2000).
Liebenthal, E., Binder, J. R., Spitzer, S. M., Possing, E. T. & Medler, D. A. Neural substrates of phonemic perception. Cereb. Cortex 15, 1621–1631 (2005).
Rodd, J. M., Davis, M. H. & Johnsrude, I. S. The neural mechanisms of speech comprehension: fmri studies of semantic ambiguity. Cereb. Cortex 15, 1261–1269 (2005).
Wagner, A. D., Paré-Blagoev, E. J., Clark, J. & Poldrack, R. A. Recovering meaning: left prefrontal cortex guides controlled semantic retrieval. Neuron 31, 329–338 (2001).
Bruneau, N. & Gomot, M. Auditory evoked potentials (n1 wave) as indices of cortical development. In Neuroimaging in child neuropsychiatric disorders, 113–123 (Springer, 1998).
Lightfoot, G. Summary of the n1-p2 cortical auditory evoked potential to estimate the auditory threshold in adults. In Seminars in hearing, vol. 37, 001–008 (Thieme Medical Publishers, 2016).
Cole, J. Prosody in context: A review. Lang. Cognit. Neurosci. 30, 1–31 (2015).
Cole, J. et al. Sound, structure and meaning: The bases of prominence ratings in english, french and spanish. J. Phonetics 75, 113–147 (2019).
Garofolo, J. S. et al. Timit acoustic-phonetic continuous speech corpus. Tech. Rep., (Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), SRI International (SRI) and Texas Instruments, Inc. (TI), 1993). https://catalog.ldc.upenn.edu/LDC93s1.
Schoppe, O., Harper, N. S., Willmore, B. D., King, A. J. & Schnupp, J. W. Measuring the performance of neural models. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 10, 10 (2016).
Hsu, A., Borst, A. & Theunissen, F. E. Quantifying variability in neural responses and its application for the validation of model predictions. Netw. Comput. Neural Syst. 15, 91–109 (2004).
Pérez, A. et al. Timing of brain entrainment to the speech envelope during speaking, listening and self-listening. Cognition 224, 105051 (2022).
Lakatos, P., Gross, J. & Thut, G. A new unifying account of the roles of neuronal entrainment. Curr. Biol. 29, R890–R905 (2019).
Ding, N., Melloni, L., Zhang, H., Tian, X. & Poeppel, D. Cortical tracking of hierarchical linguistic structures in connected speech. Nat. Neurosci. 19, 158–164 (2016).
Pellegrino, F., Coupé, C. & Marsico, E. A cross-language perspective on speech information rate. Language 87, 539–558 (2011).
Chen, C.-M. A. et al. The corollary discharge in humans is related to synchronous neural oscillations. J. Cognit. Neurosci. 23, 2892–2904 (2011).
Zheng, Z. Z., Munhall, K. G. & Johnsrude, I. S. Functional overlap between regions involved in speech perception and in monitoring one’s own voice during speech production. J. Cognit. Neurosci. 22, 1770 (2010).
O’sullivan, J. A. et al. Attentional selection in a cocktail party environment can be decoded from single-trial eeg. Cerebral Cortex 25, 1697–1706 (2015).
Power, A. J., Foxe, J. J., Forde, E.-J., Reilly, R. B. & Lalor, E. C. At what time is the cocktail party? a late locus of selective attention to natural speech. Eur. J. Neurosci. 35, 1497–1503 (2012).
Bigdely-Shamlo, N., Kreutz-Delgado, K., Kothe, C. & Makeig, S. Eyecatch: Data-mining over half a million eeg independent components to construct a fully-automated eye-component detector. In 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 5845–5848 (IEEE, 2013).
Mognon, A., Jovicich, J., Bruzzone, L. & Buiatti, M. Adjust: An automatic eeg artifact detector based on the joint use of spatial and temporal features. Psychophysiology 48, 229–240 (2011).
Tran, Y., Craig, A., Boord, P. & Craig, D. Using independent component analysis to remove artifact from electroencephalographic measured during stuttered speech. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 42, 627–633 (2004).
Muthukumaraswamy, S. D. High-frequency brain activity and muscle artifacts in meg/eeg: a review and recommendations. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 7, 138 (2013).
Janssen, N., Meij, Mvd, López-Pérez, P. J. & Barber, H. A. Exploring the temporal dynamics of speech production with eeg and group ica. Sci. Rep. 10, 3667 (2020).
Delorme, A. & Makeig, S. Eeglab, https://eeglab.org/tutorials/06_RejectArtifacts/RunICA.html (2004).
Porcaro, C., Medaglia, M. T. & Krott, A. Removing speech artifacts from electroencephalographic recordings during overt picture naming. NeuroImage 105, 171–180 (2015).
Chartier, J., Anumanchipalli, G. K., Johnson, K. & Chang, E. F. Encoding of articulatory kinematic trajectories in human speech sensorimotor cortex. Neuron 98, 1042–1054 (2018).
Gravano, A., Kamienkowski, J. E. & Brusco, P. Uba games corpus. Tech. Rep., Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET), http://hdl.handle.net/11336/191235 (2023).
Delorme, A. & Makeig, S. Eeglab: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial eeg dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 134, 9–21 (2004).
Widmann, A. & Schröger, E. Filter effects and filter artifacts in the analysis of electrophysiological data. Front. Psychol. 3, 233 (2012).
Delorme, A. & Makeig, S. Eeglab, https://eeglab.org/others/Firfilt_FAQ.html (2004).
Lee, T.-W. Independent Component Analysis: Theory and Applications (Springer-Science+Business Media, B.V., 1998).
Gramfort, A. et al. MEG and EEG data analysis with MNE-Python. Front. Neurosci. 7, 1–13 (2013).
Virtanen, P. et al. SciPy 1.0: Fundamental Algorithms for Scientific Computing in Python. Nat. Methods 17, 261–272 (2020).
McFee, B. et al. librosa: Audio and music signal analysis in python. In Proceedings of the 14th python in science conference, vol. 8, 18–25 (Citeseer, 2015).
Slaney, M. Auditory toolbox. Interval Res. Corp. Tech. Rep. 10, 1194 (1998).
Mesgarani, N., Cheung, C., Johnson, K. & Chang, E. F. Phonetic feature encoding in human superior temporal gyrus. Science 343, 1006–1010 (2014).
Marozzi, M. Some remarks about the number of permutations one should consider to perform a permutation test. Statistica 64, 193–201 (2004).
Charlier, F. et al. Statannotations. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7213391 (2022).
Mensen, A. & Khatami, R. Advanced eeg analysis using threshold-free cluster-enhancement and non-parametric statistics. Neuroimage 67, 111–118 (2013).
Kass, R. E. & Raftery, A. E. Bayes factors. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 90, 773–795 (1995).
Hoijtink, H., Mulder, J., van Lissa, C. & Gu, X. A tutorial on testing hypotheses using the bayes factor. Psychol. Methods 24, 539 (2019).
Lachaux, J.-P., Rodriguez, E., Martinerie, J. & Varela, F. J. Measuring phase synchrony in brain signals. Hum. Brain Mapp. 8, 194–208 (1999).
Source link